Summary Methods
The Clumper object also offers useful methods that aren't verbs.
Summary Methods¶
Here's a sample of useful methods to get summaries from your collection.
Each of these methods has a string equivalent that is used in .agg()
when making aggregations. We'll list a few common ones here but take note:
all of these are methods that ignore the grouping. If you want to use these
methods with grouping, use .agg() instead.
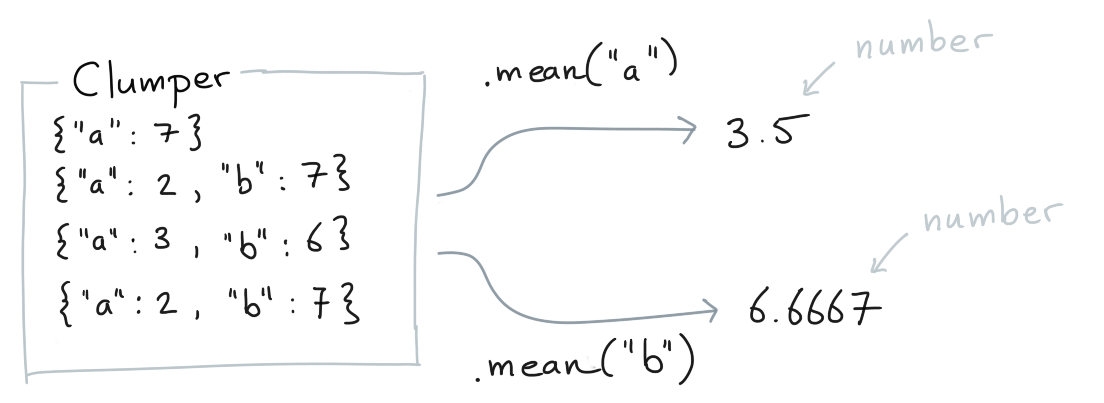
.mean()¶
You can calculate the mean of values for which a key exists.
from clumper import Clumper
list_of_dicts = [
{'a': 7},
{'a': 2, 'b': 7},
{'a': 3, 'b': 6},
{'a': 2, 'b': 7}
]
Clumper(list_of_dicts).mean("a")
Clumper(list_of_dicts).mean("b")
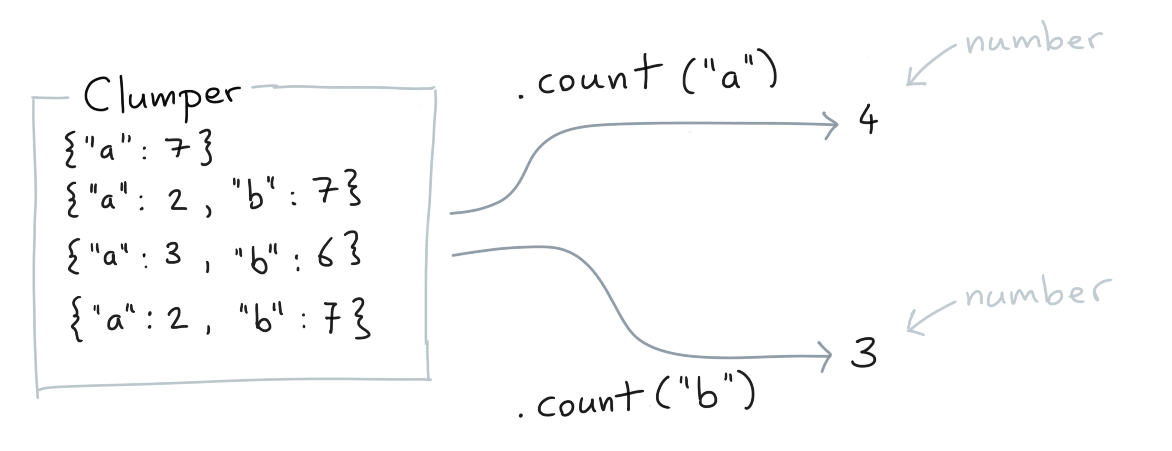
.count()¶
You can count the number of rows for which a key exists.
from clumper import Clumper
list_of_dicts = [
{'a': 7},
{'a': 2, 'b': 7},
{'a': 3, 'b': 6},
{'a': 2, 'b': 7}
]
Clumper(list_of_dicts).count("a")
Clumper(list_of_dicts).count("b")
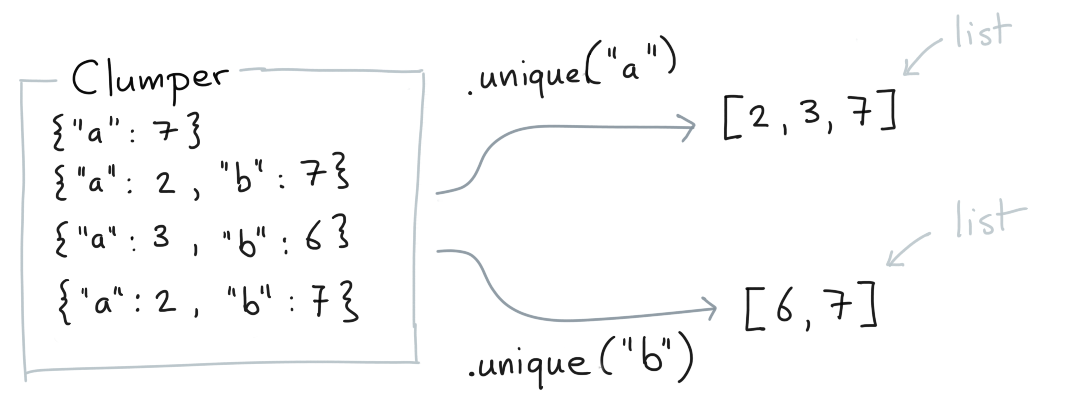
.unique()¶
You can retrieve all unique values for a certain key.
from clumper import Clumper
list_of_dicts = [
{'a': 7},
{'a': 2, 'b': 7},
{'a': 3, 'b': 6},
{'a': 2, 'b': 7}
]
Clumper(list_of_dicts).unique("a")
Clumper(list_of_dicts).unique("b")
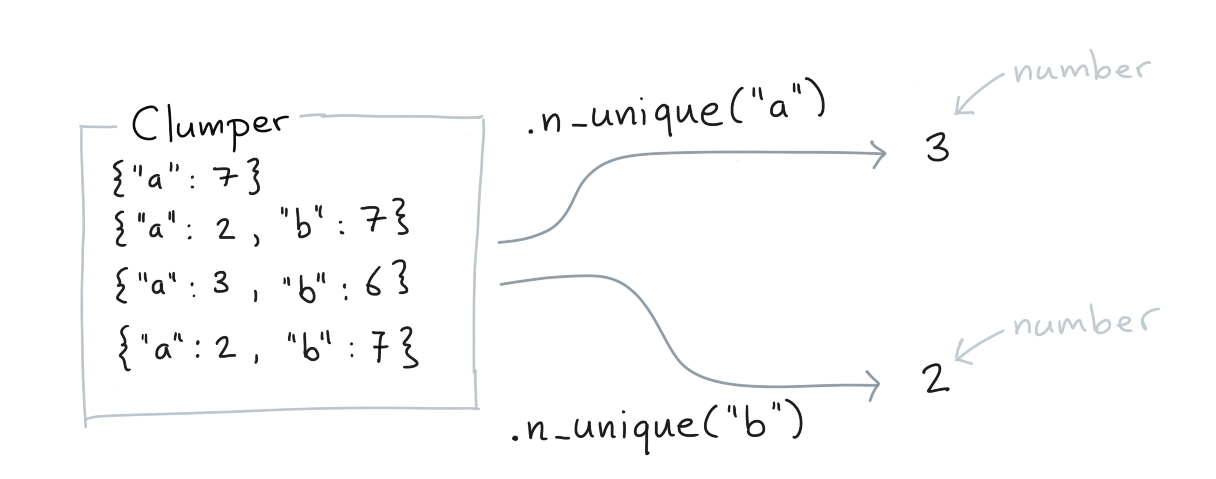
.n_unique()¶
You can the retrieve the number of unique values for a certain key.
from clumper import Clumper
list_of_dicts = [
{'a': 7},
{'a': 2, 'b': 7},
{'a': 3, 'b': 6},
{'a': 2, 'b': 7}
]
Clumper(list_of_dicts).n_unique("a")
Clumper(list_of_dicts).n_unique("b")
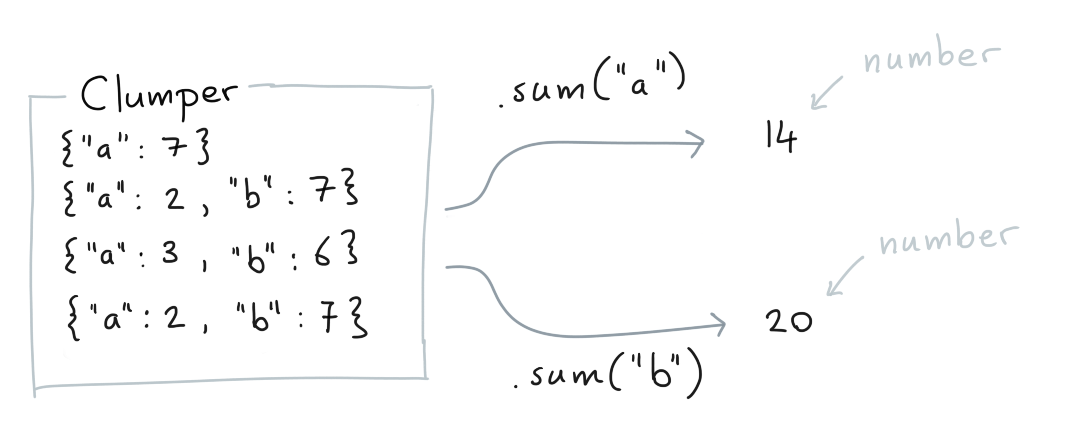
.sum()¶
You can calculate the sum of values for which a key exists.
from clumper import Clumper
list_of_dicts = [
{'a': 7},
{'a': 2, 'b': 7},
{'a': 3, 'b': 6},
{'a': 2, 'b': 7}
]
Clumper(list_of_dicts).sum("a")
Clumper(list_of_dicts).sum("b")
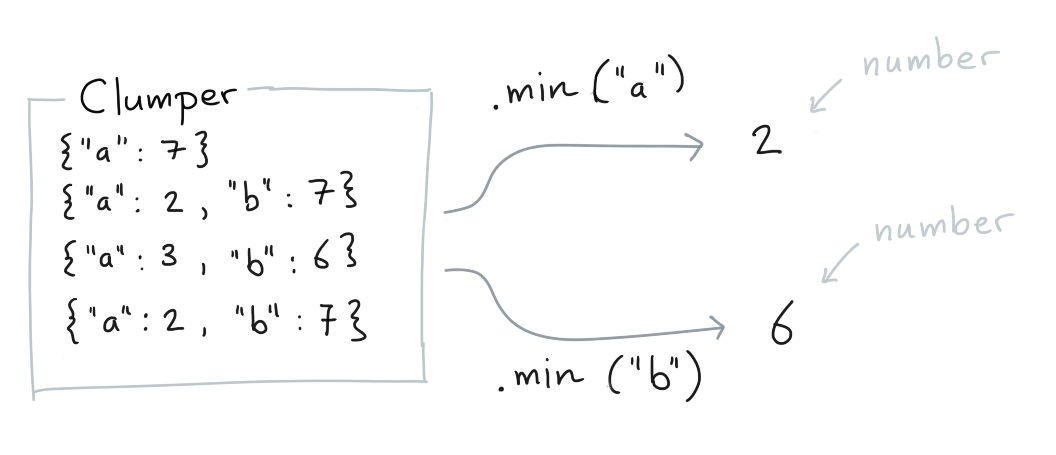
.min()¶
You can calculate the minimum of values for which a key exists.
from clumper import Clumper
list_of_dicts = [
{'a': 7},
{'a': 2, 'b': 7},
{'a': 3, 'b': 6},
{'a': 2, 'b': 7}
]
Clumper(list_of_dicts).min("a")
Clumper(list_of_dicts).min("b")
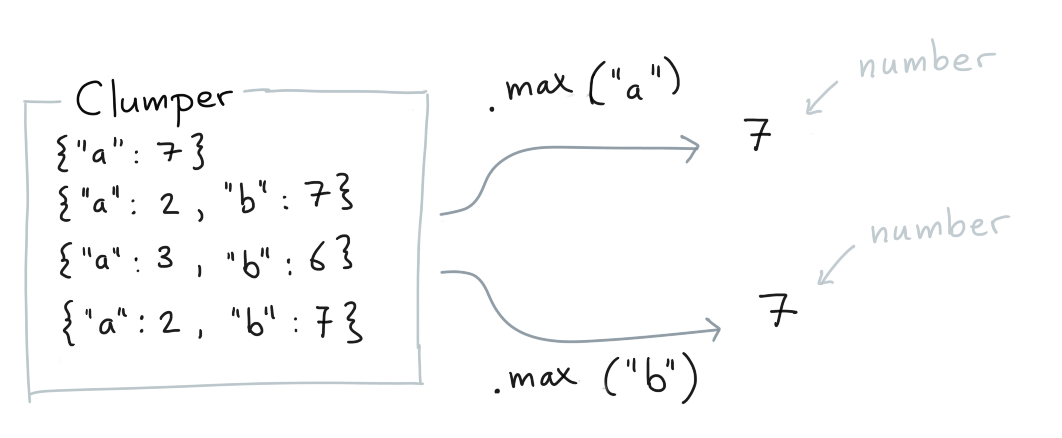
.max()¶
You can calculate the maximum of values for which a key exists.
from clumper import Clumper
list_of_dicts = [
{'a': 7},
{'a': 2, 'b': 7},
{'a': 3, 'b': 6},
{'a': 2, 'b': 7}
]
Clumper(list_of_dicts).max("a")
Clumper(list_of_dicts).max("b")
More?¶
If you'd like to see more information these methods check the API
of the Clumper object. That's where you'll find them.