Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Machine Learning Visualization#
This example demonstrates a simple machine learning workflow with visualization. The Marimo version allows interactive parameter tuning and real-time updates.
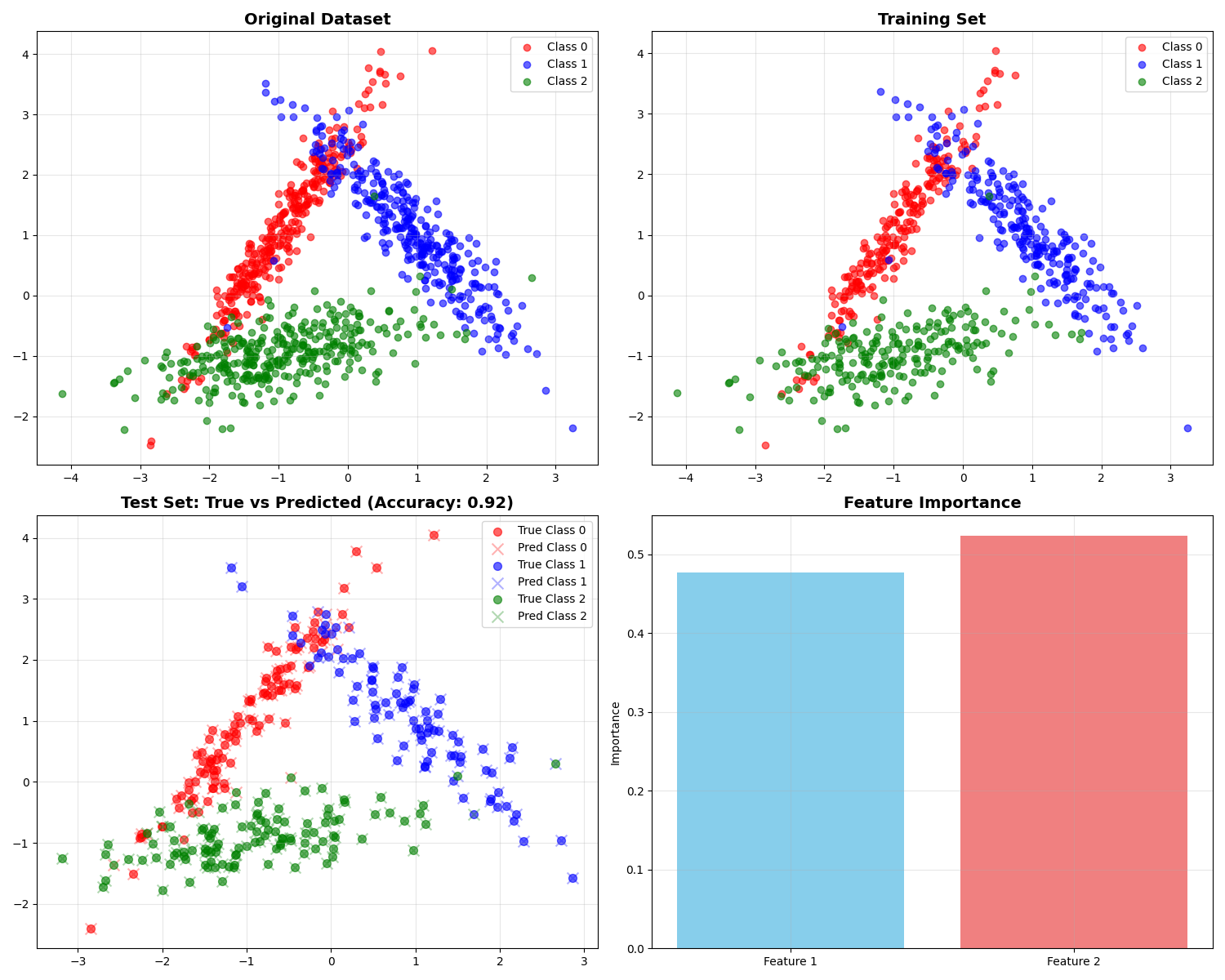
Generating synthetic classification dataset...
Training Random Forest classifier...
=== Model Performance ===
Accuracy: 0.920
Feature Importances:
Feature 1: 0.477
Feature 2: 0.523
Detailed Classification Report:
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.87 0.93 0.90 101
1 0.95 0.87 0.91 87
2 0.95 0.95 0.95 112
accuracy 0.92 300
macro avg 0.92 0.92 0.92 300
weighted avg 0.92 0.92 0.92 300
🚀 Launch in Marimo to:
• Adjust model parameters interactively
• Try different algorithms
• Modify dataset parameters
• See real-time performance updates
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, classification_report
# Generate synthetic dataset
print("Generating synthetic classification dataset...")
X, y = make_classification(
n_samples=1000,
n_features=2,
n_redundant=0,
n_informative=2,
n_clusters_per_class=1,
n_classes=3,
random_state=42
)
# Split the data
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42
)
# Train model
print("Training Random Forest classifier...")
model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Make predictions
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
# Create visualization
fig, ((ax1, ax2), (ax3, ax4)) = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(15, 12))
# Original dataset
colors = ['red', 'blue', 'green']
for i, color in enumerate(colors):
mask = y == i
ax1.scatter(X[mask, 0], X[mask, 1], c=color, alpha=0.6, label=f'Class {i}')
ax1.set_title('Original Dataset', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax1.legend()
ax1.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# Training set
for i, color in enumerate(colors):
mask = y_train == i
ax2.scatter(X_train[mask, 0], X_train[mask, 1], c=color, alpha=0.6, label=f'Class {i}')
ax2.set_title('Training Set', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax2.legend()
ax2.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# Test set with predictions
for i, color in enumerate(colors):
mask = y_test == i
ax3.scatter(X_test[mask, 0], X_test[mask, 1], c=color, alpha=0.6,
marker='o', s=50, label=f'True Class {i}')
mask_pred = y_pred == i
ax3.scatter(X_test[mask_pred, 0], X_test[mask_pred, 1], c=color, alpha=0.3,
marker='x', s=100, label=f'Pred Class {i}')
ax3.set_title(f'Test Set: True vs Predicted (Accuracy: {accuracy:.2f})',
fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax3.legend()
ax3.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# Feature importance
feature_names = ['Feature 1', 'Feature 2']
importances = model.feature_importances_
ax4.bar(feature_names, importances, color=['skyblue', 'lightcoral'])
ax4.set_title('Feature Importance', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax4.set_ylabel('Importance')
ax4.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# Print results
print("\n=== Model Performance ===")
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy:.3f}")
print(f"Feature Importances:")
for name, importance in zip(feature_names, importances):
print(f" {name}: {importance:.3f}")
print(f"\nDetailed Classification Report:")
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))
print("\n🚀 Launch in Marimo to:")
print(" • Adjust model parameters interactively")
print(" • Try different algorithms")
print(" • Modify dataset parameters")
print(" • See real-time performance updates")
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.268 seconds)